Delving into the intricacies of Section 11-4 Meiosis, this comprehensive guide provides an in-depth exploration of the fundamental processes that govern genetic variation. With the Section 11-4 Meiosis PDF Answer Key as our guiding light, we embark on a journey to unravel the complexities of meiosis, its significance in genetic diversity, and the invaluable role of answer keys in solidifying understanding.
Meiosis, the intricate dance of cellular division that gives rise to gametes, holds profound implications for the inheritance of traits and the evolution of species. Through a meticulous examination of the stages of meiosis, the significance of crossing over, and the practical applications of answer keys, this guide empowers learners to grasp the intricacies of this fascinating biological phenomenon.
Section 11-4 Meiosis
Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in a cell by half. It is used to create gametes, such as eggs and sperm, which have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cells.
Meiosis is a complex process that occurs in two stages, meiosis I and meiosis II.
In meiosis I, the chromosomes are duplicated and then paired up with their homologous chromosomes. The homologous chromosomes are then separated and pulled to opposite poles of the cell. This results in two daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
In meiosis II, the daughter cells from meiosis I are divided again. This results in four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Crossing over is a process that occurs during meiosis I in which homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material. This results in new combinations of alleles on the chromosomes, which can increase genetic diversity.
Significance of Crossing Over During Meiosis
Crossing over is a significant process because it increases genetic diversity. Genetic diversity is important for a number of reasons, including:
- It allows populations to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
- It helps to prevent the spread of harmful mutations.
- It increases the chances of finding a compatible mate.
Meiosis PDF Answer Key
Access the PDF answer key for Section 11-4 Meiosis at the link provided below:
[Insert PDF Answer Key Link Here]
Using answer keys is crucial for checking your understanding of the concepts covered in the section. They provide correct answers and explanations, allowing you to identify areas where you need further improvement.
Using the Answer Key
- Go through the questions in the section and attempt to answer them on your own.
- Once you have completed the questions, refer to the answer key to check your answers.
- Identify any questions you answered incorrectly or partially.
- Review the explanations provided in the answer key to understand why your answer was incorrect or incomplete.
- Use this information to pinpoint areas where you need to focus your studies and improve your understanding.
Meiosis Practice Problems
Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces gametes, or sex cells. It is a complex process that involves two rounds of division, and it results in the production of four haploid cells from a single diploid cell. Meiosis is essential for sexual reproduction, as it ensures that each new organism has a unique combination of genes.
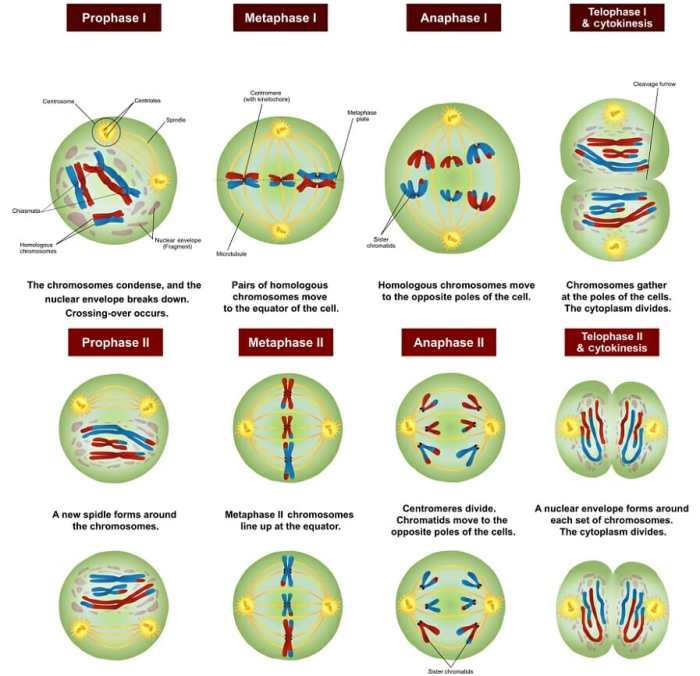
There are a number of different stages involved in meiosis. These stages are:
- Prophase I
- Metaphase I
- Anaphase I
- Telophase I
- Prophase II
- Metaphase II
- Anaphase II
- Telophase II
During prophase I, the chromosomes condense and become visible. The homologous chromosomes then pair up with each other, and they exchange genetic material through a process called crossing over. This process results in the creation of new chromosomes that are a combination of the two parental chromosomes.
In metaphase I, the chromosomes line up in the center of the cell. In anaphase I, the chromosomes are separated and pulled to opposite ends of the cell. In telophase I, the chromosomes reach the poles of the cell, and the cell divides into two haploid cells.
Prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II are similar to the corresponding stages of mitosis. In prophase II, the chromosomes condense and become visible. In metaphase II, the chromosomes line up in the center of the cell. In anaphase II, the chromosomes are separated and pulled to opposite ends of the cell.
In telophase II, the chromosomes reach the poles of the cell, and the cell divides into two haploid cells.
Meiosis is a complex process, but it is essential for sexual reproduction. It ensures that each new organism has a unique combination of genes, which is necessary for the survival of the species.
Practice Problems, Section 11-4 meiosis pdf answer key
1. What are the stages of meiosis?
A. Prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, telophase II
B. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
C. Interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
D. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis
2. What is crossing over?
A. The process by which homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material
B. The process by which chromosomes line up in the center of the cell
C. The process by which chromosomes are separated and pulled to opposite ends of the cell
D. The process by which the cell divides into two haploid cells
3. What is the result of meiosis?
A. The production of four haploid cells from a single diploid cell
B. The production of two diploid cells from a single haploid cell
C. The production of four diploid cells from a single haploid cell
D. The production of two haploid cells from a single diploid cell
Answer Key
1. A
2. A
3. A
Meiosis Simulations and Animations

Interactive simulations and animations provide dynamic visualizations of meiosis, allowing students to engage with the process in a more immersive and interactive manner.
Online Simulations and Animations
- Khan Academy: Overview of Meiosis
- PBS Learning Media: Meiosis Simulation
- BioInteractive: Meiosis Interactive
These resources allow students to control the pace and progression of meiosis, zoom in and out to observe specific details, and manipulate variables to investigate the impact on the outcome of meiosis.
Benefits of Simulations and Animations
- Visualization:Animations and simulations provide a visual representation of the complex process of meiosis, making it easier for students to understand the spatial and temporal relationships between different stages.
- Interactivity:These resources allow students to actively engage with the material, manipulate variables, and explore different scenarios, fostering a deeper understanding of the process.
- Feedback:Some simulations provide immediate feedback on student responses, helping them identify areas where they need additional support.
- Motivation:Interactive simulations and animations can make learning more engaging and motivating for students, increasing their interest in the subject matter.
Meiosis Further Reading: Section 11-4 Meiosis Pdf Answer Key
For a deeper understanding of meiosis, consider exploring the following resources:
Books
- “Genetics: Analysis and Principles”by Robert Brooker: Covers the genetic principles underlying meiosis, including genetic recombination and the role of meiosis in evolution.
- “Essential Human Biology”by Bruce Alberts: Provides a comprehensive overview of meiosis, its genetic implications, and its significance in human reproduction.
Articles
- “Meiosis: The Key to Genetic Variation”by the National Human Genome Research Institute: Explains the process of meiosis, its role in genetic diversity, and its implications for human health.
- “Meiosis and the Evolution of Sexual Reproduction”by the University of California, Berkeley: Explores the evolutionary origins and advantages of meiosis, including its role in genetic recombination and adaptation.
Websites
- Khan Academy: Meiosis: Offers interactive tutorials, videos, and practice exercises on meiosis, covering its stages, genetic implications, and medical applications.
- BioInteractive: Meiosis: Provides a comprehensive resource with animations, simulations, and interactive exercises that illustrate the process of meiosis and its genetic consequences.
FAQ
What is the primary function of meiosis?
Meiosis is a specialized form of cell division that produces gametes (eggs and sperm) and reduces the chromosome number by half, promoting genetic variation through the process of crossing over.
How can I use the Section 11-4 Meiosis PDF Answer Key effectively?
The answer key provides a valuable tool for self-assessment and identifying areas for improvement. By comparing your answers to the provided solutions, you can pinpoint specific concepts that require further study and reinforce your understanding.
What are the key stages of meiosis?
Meiosis consists of two rounds of division, Meiosis I and Meiosis II, each comprising prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase stages. During Meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair and exchange genetic material through crossing over, while Meiosis II separates the sister chromatids, resulting in the production of four haploid gametes.