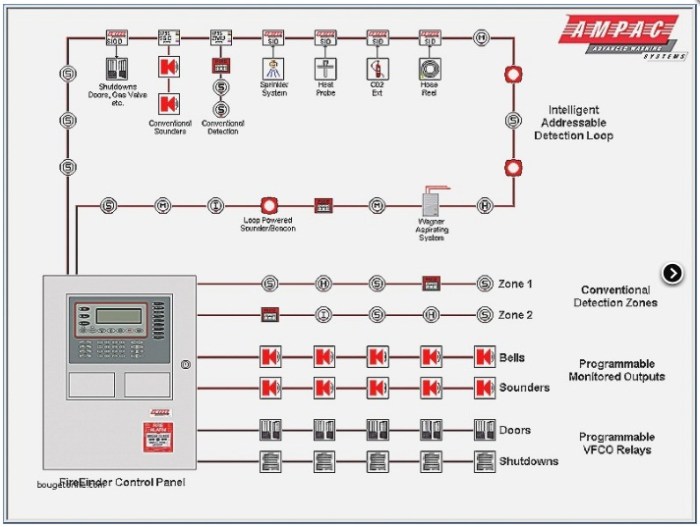
What is a signaling line circuit – Signaling line circuits, the backbone of telecommunications and networking systems, play a pivotal role in transmitting control and signaling information. This article delves into the intricacies of signaling line circuits, exploring their historical evolution, components, architecture, and diverse applications.
The concept of signaling line circuits has its roots in the early days of telegraphy, where the need arose for reliable and efficient transmission of control signals between telegraph stations. Over the years, signaling line circuits have evolved significantly, incorporating advancements in technology and adapting to the demands of modern communication systems.
1. Overview of Signaling Line Circuit: What Is A Signaling Line Circuit
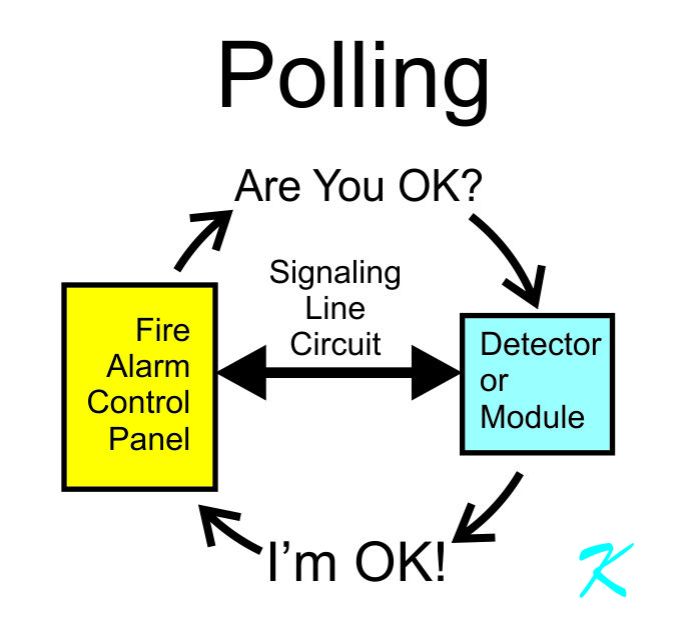
A signaling line circuit (SLC) is a communication channel that transmits signaling information between telecommunication devices, such as telephone switches and network elements. SLCs are used to establish, maintain, and terminate connections, as well as to exchange control and supervisory information.
SLCs have evolved significantly since their inception in the early days of telephony. Initially, they were simple analog circuits that used direct current (DC) signaling. However, with the advent of digital telephony, SLCs have evolved to support digital signaling protocols, such as ISDN and SS7.
2. Components and Architecture
A typical SLC consists of the following components:
- Transmitters:Convert digital signals into electrical signals that can be transmitted over the transmission line.
- Receivers:Convert electrical signals received over the transmission line into digital signals.
- Transmission lines:Physical medium over which the electrical signals are transmitted.
SLCs can be classified into two main types based on their architecture:
- Point-to-point SLCs:Connect two telecommunication devices directly.
- Multi-point SLCs:Connect multiple telecommunication devices to a single central point.
3. Types of Signaling Line Circuits
SLCs can be classified into different types based on their transmission mode, bandwidth, and protocol:
- Analog SLCs:Use analog signals to transmit data.
- Digital SLCs:Use digital signals to transmit data.
- Wideband SLCs:Support high bandwidths, typically used for transmitting data and multimedia.
- Narrowband SLCs:Support low bandwidths, typically used for transmitting voice and signaling information.
4. Applications and Use Cases
SLCs are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Telecommunications:Establishing and maintaining telephone connections.
- Networking:Connecting network devices, such as routers and switches.
- Industrial automation:Controlling and monitoring industrial processes.
- Transportation:Managing traffic signals and railway systems.
5. Design Considerations and Optimization
When designing and optimizing SLCs, the following factors should be considered:
- Signal integrity:Ensuring that the signal transmitted over the SLC is not corrupted.
- Noise immunity:Minimizing the impact of noise on the transmitted signal.
- Bandwidth requirements:Selecting the appropriate bandwidth for the application.
6. Troubleshooting and Maintenance, What is a signaling line circuit
Common troubleshooting techniques for SLCs include:
- Loop testing:Checking the continuity of the SLC.
- Signal tracing:Identifying the point at which a signal is lost.
- Bit error rate testing:Measuring the number of errors in the transmitted signal.
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the reliability of SLCs. This includes:
- Cleaning and inspecting connectors:
- Testing and calibrating equipment:
- Replacing faulty components:
7. Future Trends and Advancements
Emerging trends in SLC technology include:
- Software-defined networking (SDN):Enabling the programmability and control of SLCs through software.
- Network virtualization:Creating virtual SLCs that can be dynamically provisioned and managed.
- 5G technology:Supporting high-bandwidth and low-latency SLCs for mobile communications.
Expert Answers
What is the primary purpose of a signaling line circuit?
The primary purpose of a signaling line circuit is to transmit control and signaling information between communication devices, enabling the establishment, maintenance, and termination of communication sessions.
What are the key components of a signaling line circuit?
The key components of a signaling line circuit typically include transmitters, receivers, transmission lines, and signal processing equipment.
What are the different types of signaling line circuits?
Signaling line circuits can be classified into various types based on transmission mode (analog or digital), bandwidth, and protocol (e.g., TDM, ATM, Ethernet).