Wheezing and hives are symptoms of servsafe – Wheezing and hives, seemingly innocuous symptoms, take on a graver significance when linked to foodborne illness. This article delves into the intricate relationship between these symptoms and foodborne pathogens, shedding light on their importance in the context of food safety.
Food allergies, intolerances, and histamine reactions can trigger wheezing and hives. Understanding these triggers is crucial for individuals at risk and those responsible for ensuring food safety.
1. Introduction

Wheezing, characterized by a whistling sound during breathing, and hives, raised itchy bumps on the skin, are potential symptoms of foodborne illness. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for food safety professionals, as they can indicate a reaction to contaminated or allergenic food.
2. Causes of Wheezing and Hives
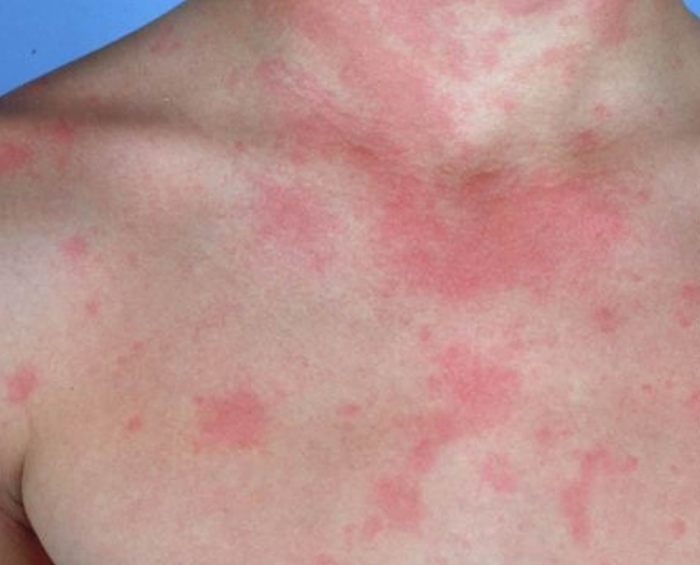
Wheezing and hives can result from various causes, including:
- Food allergies and intolerances:These reactions occur when the body’s immune system overreacts to specific food proteins.
- Histamine and other immune responses:Foodborne pathogens or toxins can trigger the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators, leading to wheezing and hives.
- Medications and other triggers:Certain medications, such as aspirin and ibuprofen, and environmental factors like pollen or insect bites can also cause these symptoms.
3. Wheezing and Hives as Symptoms of Foodborne Illness: Wheezing And Hives Are Symptoms Of Servsafe
Wheezing and hives can be symptoms of several foodborne illnesses, including:
- Food poisoning:Caused by bacteria like Salmonellaand E. coli, leading to nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, along with potential wheezing and hives.
- Scombroid poisoning:Consuming spoiled fish containing high levels of histamine, resulting in symptoms such as facial flushing, wheezing, and hives.
- Shellfish poisoning:Eating contaminated shellfish can cause paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) or neurotoxic shellfish poisoning (NSP), leading to neurological symptoms, including difficulty breathing and hives.
Symptom onset typically occurs within hours of ingesting contaminated food.
4. Diagnosis and Treatment
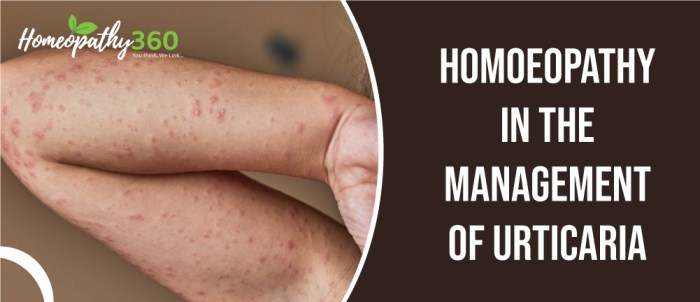
If you experience wheezing and hives after eating, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Diagnosis involves a physical examination, medical history, and potential allergy testing. Treatment options may include:
- Antihistamines:Medications that block histamine and reduce allergic reactions.
- Bronchodilators:Inhalers or nebulizers that open up airways and relieve wheezing.
- Epinephrine:In severe cases, epinephrine may be administered to counteract anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic reaction.
5. Prevention and Control
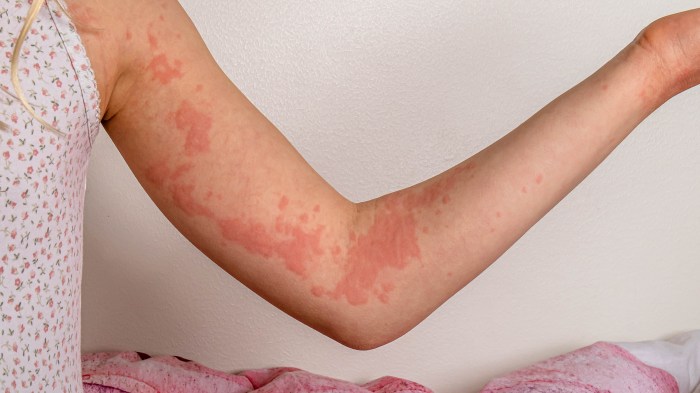
Preventing foodborne illness and the associated symptoms of wheezing and hives is essential. Key measures include:
- Food safety practices:Adhering to proper food handling, storage, and cooking techniques to minimize contamination.
- Allergen avoidance:Identifying and avoiding foods that trigger allergic reactions.
- Proper food handling and storage:Ensuring proper food handling, refrigeration, and storage to prevent bacterial growth.
Common Queries
What are the most common foodborne illnesses associated with wheezing and hives?
Salmonella, E. coli, and norovirus are among the common foodborne pathogens that can cause these symptoms.
How long after ingesting contaminated food can wheezing and hives occur?
Symptoms can manifest within minutes to several hours after consumption, depending on the pathogen and individual sensitivity.
What is the importance of seeking medical attention for wheezing and hives related to foodborne illness?
Prompt medical evaluation is crucial to rule out other underlying conditions, determine the specific pathogen, and receive appropriate treatment.