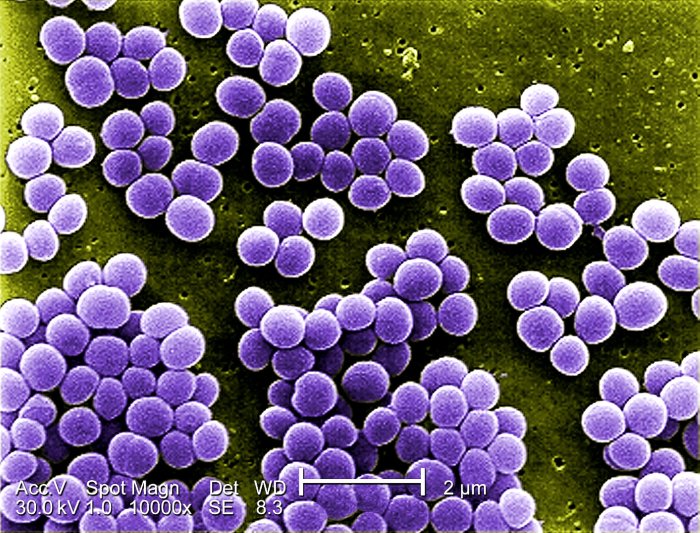
Staphylococcus aureus under microscope 1000x reveals a fascinating world of microbial structure and function. This Gram-positive bacterium, known for its pathogenicity and antibiotic resistance, exhibits distinct characteristics that set it apart from other bacterial species. Join us as we delve into the microscopic realm of Staphylococcus aureus, exploring its morphology, virulence factors, and clinical significance.
Under the high magnification of a microscope, Staphylococcus aureus presents a characteristic spherical shape, arranged in grape-like clusters. Its Gram-positive staining property, which retains the crystal violet dye, is a key diagnostic feature. This bacterium’s unique cell wall composition and virulence factors contribute to its ability to cause a wide range of infections, from skin and soft tissue infections to more severe systemic diseases.
Staphylococcus aureus under Microscope 1000x
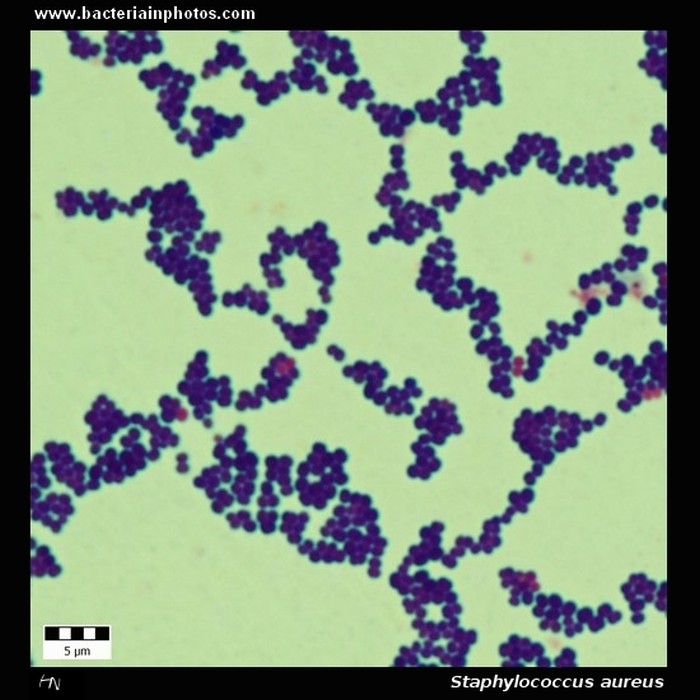
Staphylococcus aureusis a Gram-positive bacterium that is commonly found on the skin and in the nose of healthy individuals. Under a microscope at 1000x magnification, S. aureusappears as round or oval-shaped cocci that are arranged in grape-like clusters.
Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus under Microscope
Staphylococcus aureusis a Gram-positive bacterium, which means that it retains the Gram stain due to the thick peptidoglycan layer in its cell wall. This characteristic distinguishes S. aureusfrom Gram-negative bacteria, which do not retain the Gram stain and appear pink or red under a microscope.
S. aureusis also characterized by its ability to produce golden-yellow pigment, which gives it its name ( aureusmeans “golden” in Latin). This pigment is responsible for the yellow or orange color of S. aureuscolonies on agar plates.
Colony Morphology and Growth Patterns, Staphylococcus aureus under microscope 1000x
On agar plates, S. aureuscolonies are typically round, smooth, and raised. They may be pigmented yellow, orange, or white, depending on the strain. S. aureusis a facultative anaerobe, meaning that it can grow in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. It is also relatively salt-tolerant and can grow in high salt concentrations.
Clarifying Questions
What is the typical appearance of Staphylococcus aureus under a microscope?
Under 1000x magnification, Staphylococcus aureus appears as spherical bacteria arranged in grape-like clusters, with a Gram-positive staining characteristic.
How does Staphylococcus aureus cause infections?
Staphylococcus aureus possesses various virulence factors, including toxins, enzymes, and adhesion factors, which enable it to invade host tissues, evade immune defenses, and cause disease.
What is the significance of antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus?
Antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus is a major concern as it can render commonly used antibiotics ineffective, leading to prolonged infections and increased mortality.