Each firm in a monopolistically competitive market – In a monopolistically competitive market, each firm operates with a unique blend of market power and competition. This market structure, characterized by numerous sellers offering differentiated products, presents a fascinating interplay of firm-level strategies and market dynamics. Delving into the intricacies of each firm’s behavior, we explore the profit-maximizing output, product differentiation, and the role of advertising in this dynamic market environment.
Market Structure and Characteristics: Each Firm In A Monopolistically Competitive Market

A monopolistically competitive market is a market structure characterized by many small firms producing differentiated products. Each firm has a small market share and faces competition from other firms offering similar but not identical products. This market structure is distinct from both perfect competition and monopoly.
In perfect competition, firms produce identical products and there are many buyers and sellers. In a monopoly, there is only one seller in the market. Monopolistic competition falls between these two extremes, with firms producing differentiated products and facing some competition from other firms.
Similarities and Differences between Monopolistic Competition and Perfect Competition
- Similarities:Many buyers and sellers, freedom of entry and exit
- Differences:Product differentiation, downward-sloping demand curve for each firm, non-price competition
Examples of Industries that Exhibit Monopolistic Competition, Each firm in a monopolistically competitive market
- Restaurants
- Retail stores
- Clothing stores
- Furniture stores
Firm-Level Analysis
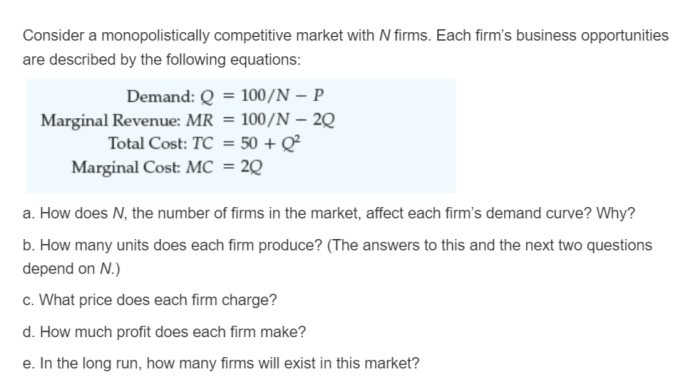
Profit-Maximizing Output and Price
In monopolistic competition, each firm maximizes profits by setting marginal revenue equal to marginal cost. This is the same profit-maximizing rule as in perfect competition, but the demand curve facing each firm in monopolistic competition is downward-sloping due to product differentiation.
Product Differentiation
Product differentiation is a key feature of monopolistic competition. Products are differentiated if they are perceived by consumers to be different from other products in the market. Differentiation can be based on a variety of factors, such as quality, features, design, and brand.
Role of Advertising and Marketing
Advertising and marketing play an important role in monopolistic competition. Firms use advertising and marketing to create product awareness, build brand loyalty, and differentiate their products from those of their competitors.
Market Equilibrium
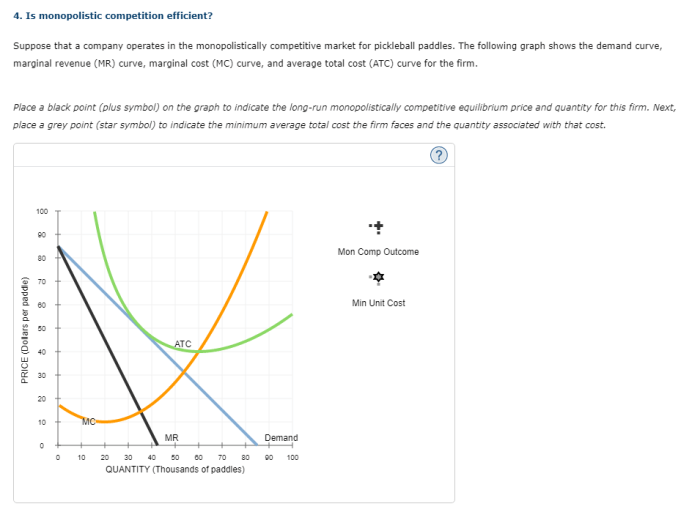
Interaction of Firms
In monopolistic competition, firms interact to determine the market equilibrium price and quantity. Each firm sets its price and output level based on the actions of its competitors. The equilibrium price and quantity are determined by the intersection of the market demand curve and the market supply curve.
Welfare Implications
Monopolistic competition is generally considered to be less efficient than perfect competition. This is because firms in monopolistic competition have some market power, which allows them to set prices above marginal cost. This results in a deadweight loss, which is a loss of consumer surplus and producer surplus.
Government Policies
Government policies can affect the structure of monopolistically competitive markets. For example, antitrust laws can be used to prevent firms from engaging in anti-competitive behavior, such as collusion or predatory pricing. Government subsidies can also be used to promote entry into monopolistically competitive markets.
Long-Run Analysis
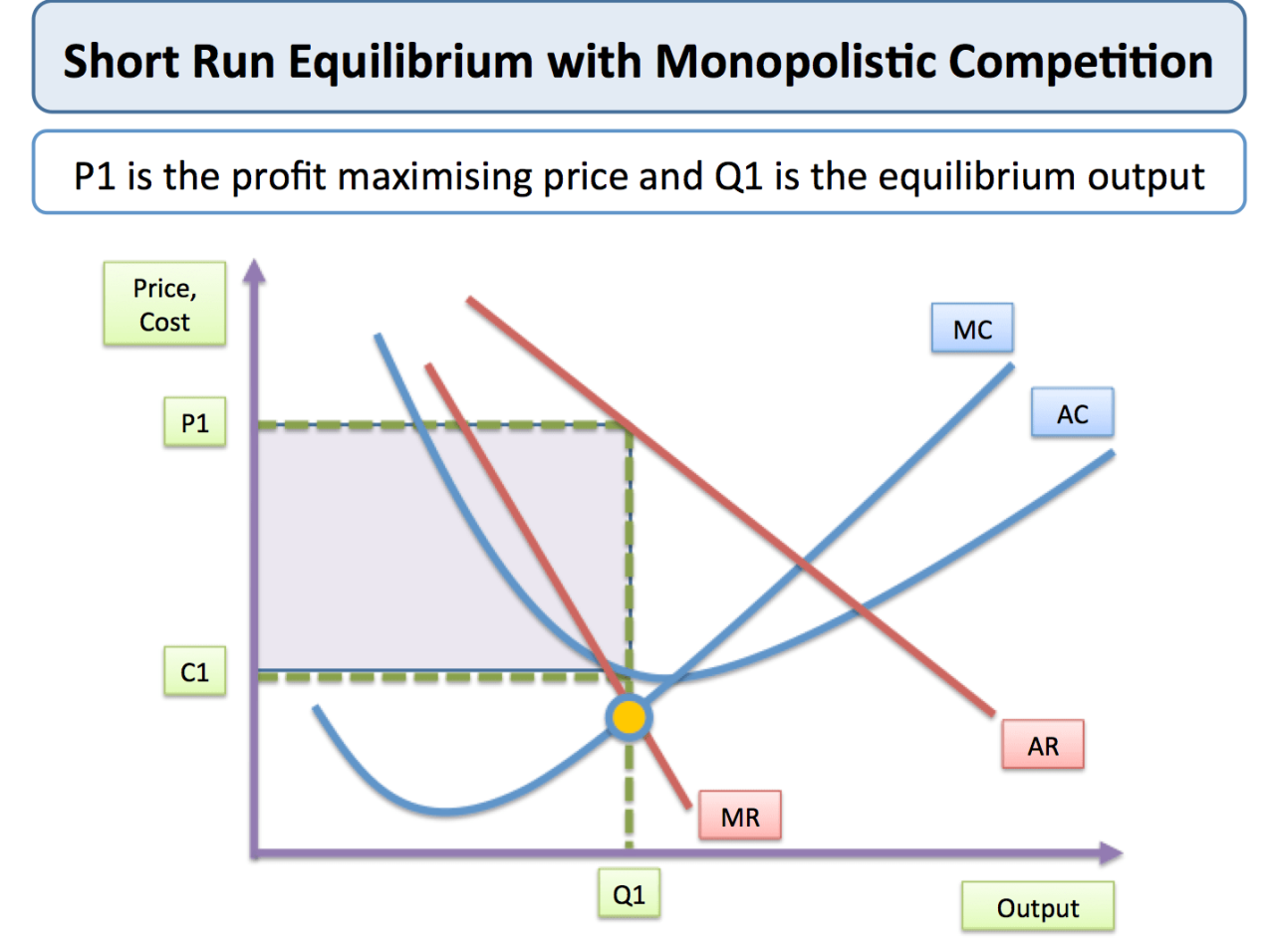
Entry and Exit
Entry and exit are important factors in monopolistic competition. In the long run, firms will enter the market if they believe they can make a profit. Firms will exit the market if they are losing money.
Number of Firms
The number of firms in a monopolistically competitive market is determined by the balance between entry and exit. In the long run, the number of firms will be such that the average firm is making zero economic profit.
Technological Change and Innovation
Technological change and innovation can affect the structure and performance of monopolistically competitive markets. New technologies can lead to the entry of new firms and the exit of old firms. Innovation can also lead to product differentiation and changes in the demand for existing products.
FAQ Resource
What is the key difference between monopolistic competition and perfect competition?
In monopolistic competition, firms possess some market power due to product differentiation, while in perfect competition, firms are price takers with identical products.
How does product differentiation affect firm behavior?
Product differentiation allows firms to charge a price premium and target specific consumer segments, influencing output and marketing strategies.
What role does advertising play in monopolistic competition?
Advertising is crucial for firms to communicate product differentiation, build brand loyalty, and influence consumer preferences.